Transforming Compliance: From Cost Centre to Growth Catalyst in 2025
Compliance as a Growth Engine: Transforming Challenges into Opportunities
As we step into 2025, the compliance landscape is witnessing a dramatic shift. Once viewed as a burdensome obligation, compliance is now being redefined as a powerful enabler of growth and innovation, particularly for startups and small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs). Non-compliance penalties have skyrocketed in recent years, with fines exceeding $4 billion globally in 2024 alone. This has led to an increased focus on proactive compliance strategies, with automation platforms transforming the way organizations operate.
The Paradigm Shift: Compliance as a Strategic Asset
“Compliance is no longer about ticking boxes; it’s about opening doors,” says Jane Doe, Chief Compliance Officer at TechInnovate Inc. This shift in perspective is evident across industries. Consider StartupX, a fintech company that revamped its compliance strategy:
- Before: Six months to achieve SOC 2 compliance, requiring three full-time employees.
- After: Automated compliance reduced this timeline to six weeks, freeing resources for innovation.
- Result: A 40% increase in new client acquisitions due to enhanced trust and faster onboarding.
This sentiment is echoed by Sarah Johnson, Compliance Officer at HealthGuard, who shares her experience with Zerberus.ai:
“Zerberus.ai has revolutionized our approach to compliance management. It’s a game changer for startups and SMEs.”
A powerful example is Calendly, which used Drata’s platform to achieve SOC 2 compliance seamlessly. Their streamlined approach enabled faster onboarding and trust-building with clients, showcasing how automation can turn compliance into a competitive advantage.
The Role of Technology in Redefining Compliance
Advancements in technology are revolutionizing compliance processes. Tools powered by artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and blockchain are streamlining workflows and enhancing effectiveness:
- AI-driven tools: Automate evidence collection, identify risks, and even predict potential compliance issues.
- ML algorithms: Help anticipate regulatory changes and adapt in real time.
- Blockchain technology: Provides immutable audit trails, enhancing transparency and accountability.
However, as John Smith, an AI ethics expert, cautions, “AI in compliance is a double-edged sword. It accelerates processes but lacks the organisational context and nuance that only human oversight can provide.”
Compliance Automation: A Booming Industry
The compliance automation tools market is experiencing rapid growth:
- 2024 market value: $2.94 billion
- Projected 2034 value: $13.40 billion
- CAGR (2024–2034): 16.4%
This surge is driven by a growing demand for integrating compliance early in business processes, a methodology dubbed “DevSecComOps.” Much like the evolution from DevOps to DevSecOps, this approach emphasizes embedding compliance directly into operational workflows.
Innovators Leading the Compliance Revolution
Old-School GRC Platforms
Traditional Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) platforms have served as compliance cornerstones for years. While robust, they are often perceived as cumbersome and less adaptable to the needs of modern businesses:
- IBM OpenPages: A legacy platform offering comprehensive risk and compliance management solutions.
- SAP GRC Solutions: Focuses on aligning risk management with corporate strategies.
- ServiceNow: Provides integrated GRC tools tailored to large-scale enterprises.
- Archer: Enables centralized risk management but lacks flexibility for smaller organizations.
New-Age Compliance Automation Suites
Emerging SaaS platforms are transforming compliance with real-time monitoring, automation, and user-friendly interfaces:
- Drata: Offers end-to-end automation for achieving and maintaining SOC 2, ISO 27001, and other certifications.
- Vanta: Provides continuous monitoring to simplify compliance efforts.
- Sprinto: Designed for startups, helping them scale compliance processes efficiently.
- Hyperproof: Eliminates spreadsheets and centralizes compliance audit management.
- Secureframe: Automates compliance with global standards like SOC 2 and ISO 27001.
Cybersecurity and Compliance Resilience Platforms
These platforms integrate compliance with cybersecurity and insurance features to address a broader spectrum of organizational risks:
- Kroll: Offers cyber resilience solutions, incident response, and digital forensics.
- Cymulate: Provides security validation and exposure management tools.
- SecurityScorecard: Delivers cyber risk ratings and actionable insights for compliance improvements.
Compliance as a Competitive Edge
A robust compliance framework delivers tangible business benefits:
- Enhanced trust: Strong compliance practices build confidence among stakeholders, including customers, partners, and investors.
- Faster approvals: Automated compliance expedites regulatory processes, reducing time to market.
- Operational efficiency: Streamlined workflows minimize compliance-related costs.
- Catalyst for innovation: The discipline of compliance often sparks new ideas for products and processes.
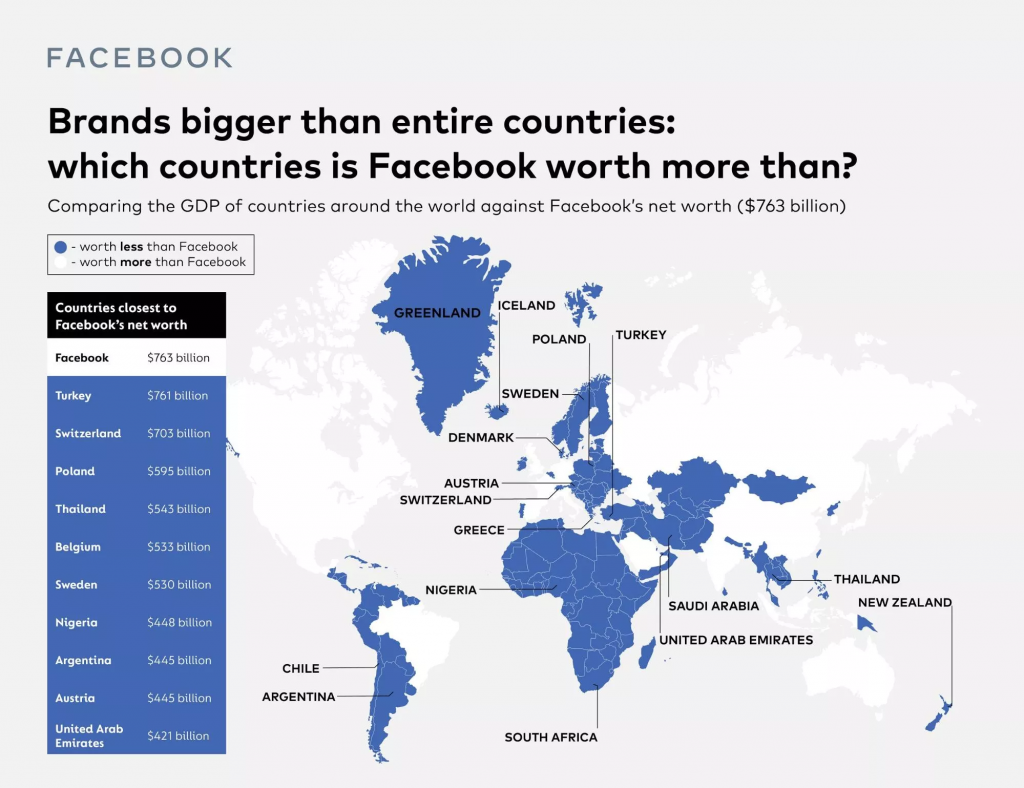
Missed Business: Quantifying the Cost of Non-Compliance
Recent data highlights the significant opportunity cost of non-compliance. Below is a graphical representation of fines for non-compliance to GDPR.
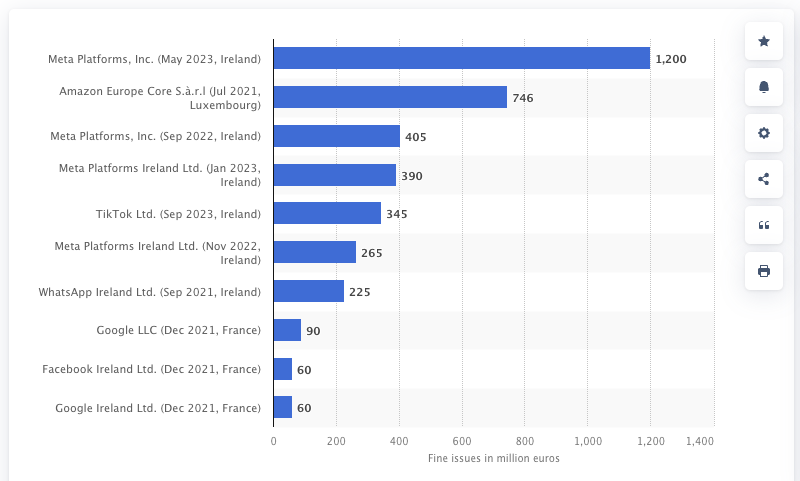
Highest fines issued for General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) violations as of January 2024 – (c) Statista. Source: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1133337/largest-fines-issued-gdpr/
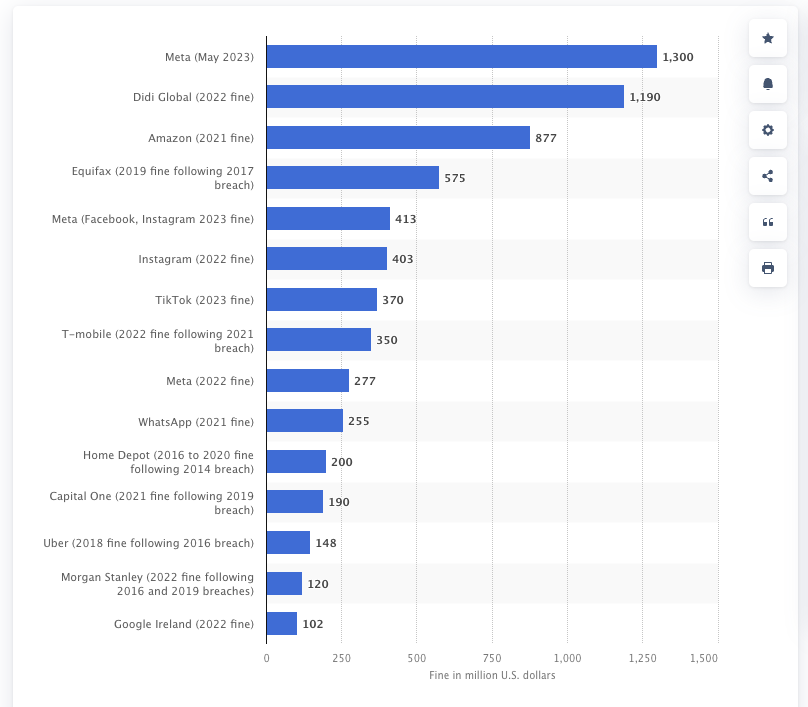
Largest data privacy violation fines, penalties, and settlements worldwide as of April 2024 (c) Statista. Source: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1170520/worldwide-data-breach-fines-settlements/
This visual underscores the importance of compliance as a protective and growth-enhancing strategy.
Missed Business: Quantifying the Cost of Non-Compliance
Recent data highlights the significant opportunity cost of non-compliance. Below is a graphical representation of how fines have impacted the revenue of companies:
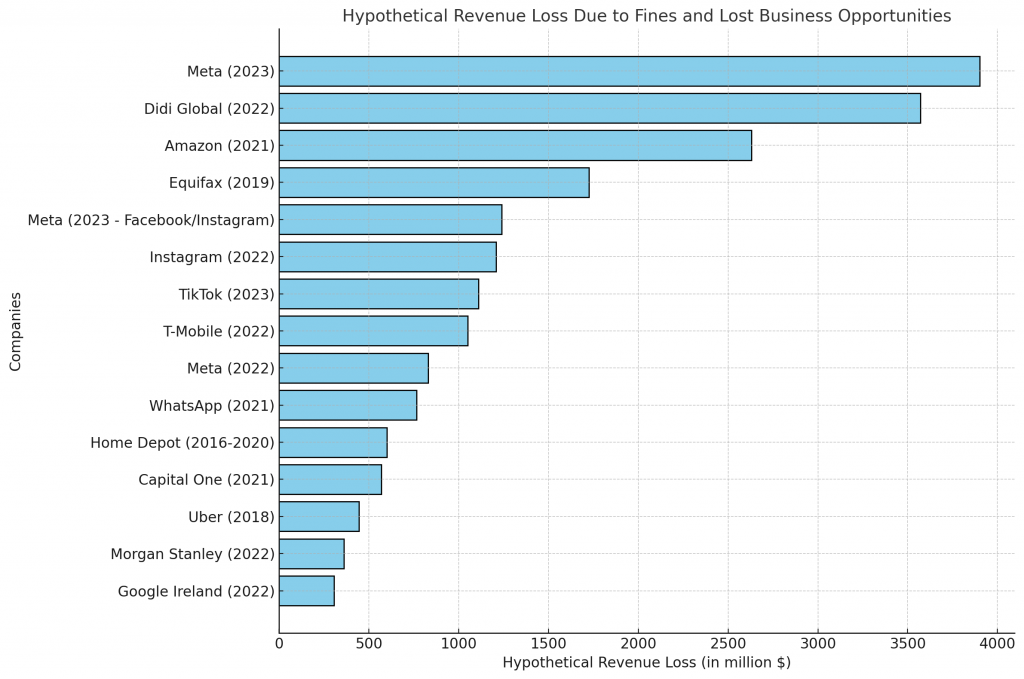
Note: Revenue loss is estimated at 3x the fines incurred, factoring in indirect costs such as reputational damage, customer attrition, and opportunity costs that amplify the financial impact.
Emerging Trends in Compliance for 2025
As we move further into 2025, several trends are reshaping the compliance landscape:
- Mandatory ESG disclosures: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting is transitioning from voluntary to mandatory, requiring organisations to establish robust frameworks.
- Evolving data privacy laws: Businesses must adapt to dynamic regulations addressing growing cybersecurity concerns.
- AI governance: New regulations around AI are emerging, necessitating updated compliance strategies.
- Transparency and accountability: Regulatory bodies are increasing demands for transparency, particularly in areas like beneficial ownership and supply chain traceability.
- Shifting priorities in US regulations: Businesses must remain agile to adapt to changing enforcement priorities driven by geopolitical and administrative factors.
Conclusion
“The future belongs to those who view compliance not as a barrier, but as a bridge to new possibilities,” concludes Sarah Johnson, CEO of CompliTech Solutions. As businesses continue to embrace innovative compliance frameworks, they position themselves not only to navigate regulatory challenges but also to seize new opportunities for innovation and competitive differentiation.
Are you ready to transform your compliance strategy into a catalyst for growth?
References
- Athennian (2024). Your 2025 Compliance Roadmap: Key Trends and Changes. Available at: https://www.athennian.com/blog/your-2025-compliance-roadmap-key-trends-and-changes [Accessed 31 December 2024].
- Ethisphere (2024). 2024 Ethics and Compliance Recap: Insights and Key Trends Shaping 2025. Available at: https://ethisphere.com/2024-ethics-and-compliance-recap/ [Accessed 31 December 2024].
- Finextra (2024). What’s happened to regulatory compliance in 2024, and how could this shape 2025 strategies? Available at: https://www.finextra.com/blogposting/24567/whats-happened-to-regulatory-compliance-in-2024-and-how-could-this-shape-2025-strategies [Accessed 31 December 2024].
- Drata (2024). Customer Success Story: Calendly. Available at: https://drata.com/customers/calendly [Accessed 31 December 2024].
- Future Data Stats (2024). Compliance Management Software Market Size & Industry Growth. Available at: https://futuredatastats.com/compliance-management-software-market/ [Accessed 31 December 2024].
- Verified Market Research (2024). Compliance Management Software Market Size & Forecast. Available at: https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/product/compliance-management-software-market/ [Accessed 31 December 2024].