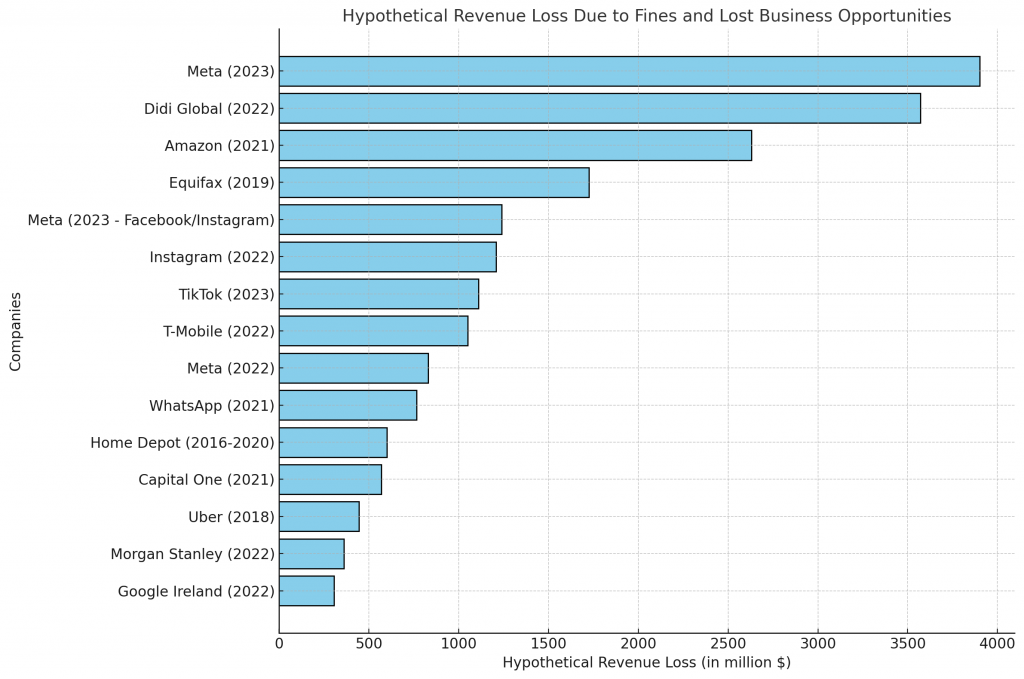
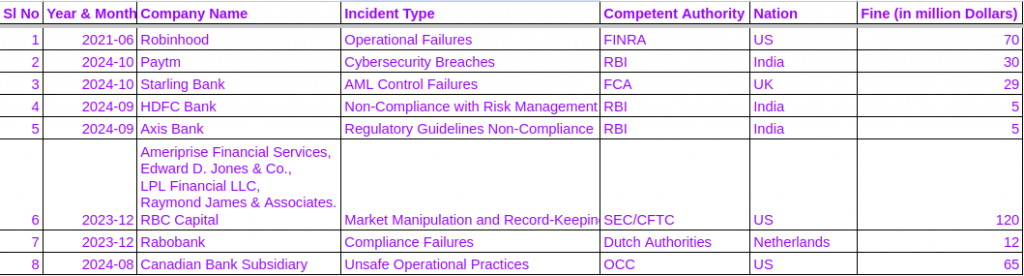
Why VCs in Europe Are Looking at Compliance Startups Now
Introduction
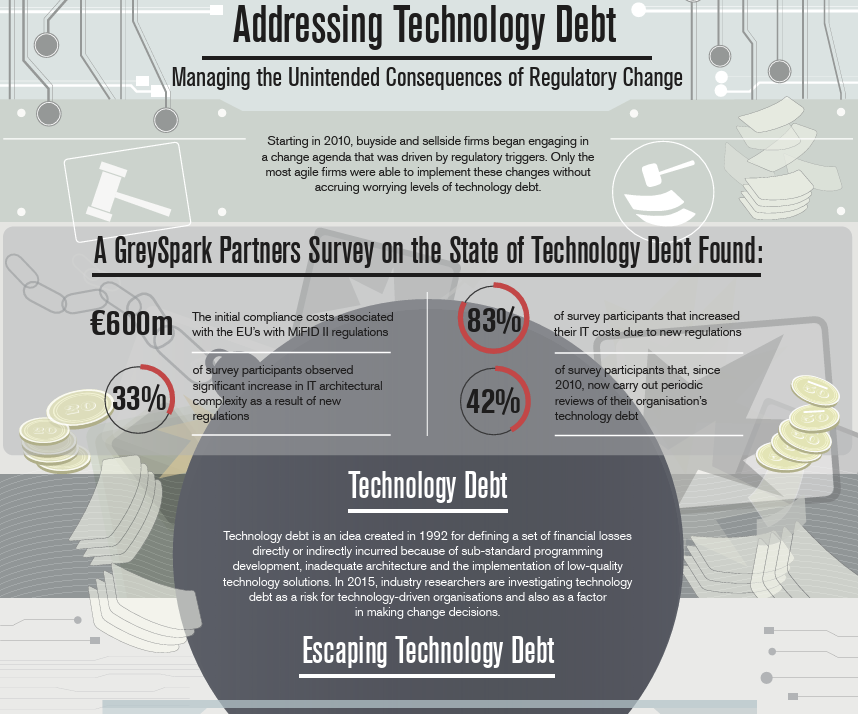
Europe’s compliance landscape is undergoing a seismic shift. With the proliferation of AI-driven products, tightening regulations such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, and PCI DSS, and the growing complexity of digital operations, businesses are under unprecedented pressure to stay compliant. Compliance automation and RegTech startups are rising to meet this challenge, infusing artificial intelligence and automation into compliance and security workflows. This transformation is not only streamlining operations but is also attracting significant venture capital (VC) investment, positioning compliance automation as a critical pillar of the modern digital economy.
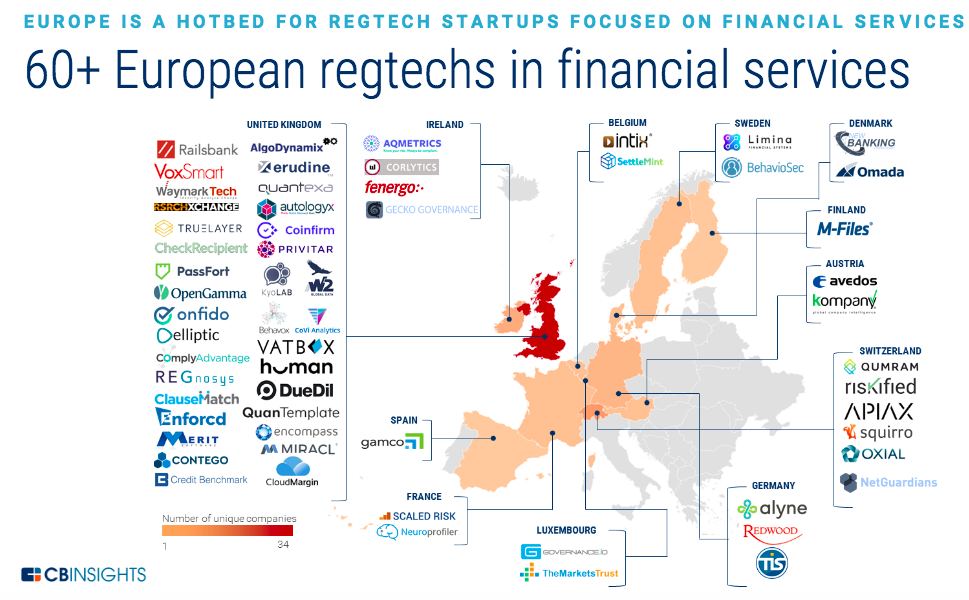
Image Source: CB Insights
1. Companies Driving Compliance Automation
1.1 Fintech and Sector-Specific Leaders
- Dotfile (France): Provides AI-powered KYB and AML automation for fintechs. Recently raised €6 million from Seaya Ventures and serves over 50 customers in 10 countries.
- REMATIQ (Germany): Specialises in MedTech compliance automation (MDR, FDA). Raised €5.4 million in seed funding led by Project A Ventures.
- Duna (Netherlands): Simplifies business identity and compliance. Raised €10.7 million with backing from Stripe and Adyen executives.
- 1.2 ISO 27001, SOC 2, PCI DSS and European Startups
| Standard | Company | Description | Funding Highlights |
| ISO 27001 | Vanta | Automates ISO 27001, SOC 2, PCI DSS audits with AI-driven evidence collection; 8,000+ clients including Atlassian. | $268M total funding (2024) |
| Scytale | AI-based ISO 27001 certification acceleration. | Undisclosed | |
| Strike Graph | Focus on ISO 27001 and SOC 2 with 100% audit success rate. | $8M Series A (2021) | |
| SOC 2 | Secureframe | AI-driven SOC 2 and ISO 27001 compliance automation. | $74M total funding (2022) |
| Sprinto | European-founded, automates SOC 2, ISO 27001, GDPR, PCI DSS, HIPAA, and more; tailored for fast-growing companies and SMBs. | $31.8M total funding (2024)6 8 9 | |
| Trustero | AI-powered SOC 2 and ISO 27001 automation, reducing audit costs by 75%. | $10.35M Series A (2024) | |
| PCI DSS | Mindsec | PCI DSS automation with faster certification cycles. | Early stage, undisclosed |
| Vanta | Also supports PCI DSS compliance automation. | Included in total funding above |
2. The VC Landscape: Who’s Investing in Compliance Automation and RegTech?
2.1 Key VC Funds and Investment Initiatives
- European Cybersecurity Investment Platform (ECIP):
- Target size: €1 billion fund-of-funds, focused on European cybersecurity and RegTech startups, especially Series A+ and late-stage companies.
- Supported by the European Investment Bank (EIB), European Commission, and major private investors.
- ECCC (European Cybersecurity Competence Centre):
- Allocated €390 million for cybersecurity projects (2025–2027), including AI, compliance automation, and post-quantum security.
- EU Digital Europe Programme:
- €1.3 billion allocated for cybersecurity and AI projects (2025–2027), with €441.6 million specifically for cybersecurity initiatives.
- Focus areas: AI-driven compliance, cyber resilience, and automation for SMEs and critical infrastructure.
- 2.2 Leading VC Funds Investing in Cybersecurity & Compliance Automation
| Fund/Initiative | Focus | Typical Ticket Size | Notable Investments(2022–2025) |
| Seaya Ventures | Fintech, compliance automation | €4–12M (Series A/B) | Dotfile, REMATIQ |
| Project A Ventures | AI, MedTech, compliance | €5–15M (Seed/Series A) | REMATIQ |
| Accel, Elevation Capital | RegTech, SaaS, security | $5–20M | Sprinto |
| CrowdStrike, Goldman Sachs | Security, compliance automation | $10–100M | Vanta |
| Accomplice Ventures | Security, SaaS | $5–20M | Secureframe |
| Bright Pixel Capital | AI, compliance, automation | $5–15M | Trustero |
- 2.3 Investment Volumes and Trends (2022–2025)
- Over $500 million invested in European compliance automation and RegTech startups in 2024 alone.
- ECIP and the ECCC have committed over €1.3 billion for cybersecurity, AI, and compliance automation projects between 2025–2027.
- VC funds are increasingly targeting multi-framework compliance automation platforms (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC 2, PCI DSS, GDPR) for their scalability and cross-sector appeal.
- 3. Regulatory Acts and Frameworks Driving Adoption
| Regulation/Act | Focus Area | Impact on Compliance Automation Startups |
| EU AI Act (2024) | Risk-based regulation of AI systems | Requires conformity assessments, external audits, AI literacy tools. |
| EU AML Package & AMLA (2025) | Stricter AML rules and new supervisory authority | Drives demand for automated AML/KYC solutions (e.g., Dotfile). |
| MiFID II & PSD3 (2025 updates) | Financial services and open banking | Pushes adoption of advanced compliance tools in fintech. |
| Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) | Crypto asset licensing and transparency | Spurs crypto compliance automation (e.g., Duna). |
| CSRD (2025) | ESG reporting and sustainability disclosures | Expands compliance scope, increasing demand for automation in ESG reporting. |
| NIS2 Directive (2024) | Cybersecurity for critical infrastructure | Boosts adoption of ISO 27001 and SOC 2 automation tools. |
| GDPR, CCPA, PIPEDA | Data protection and privacy | Necessitates automated workflows for compliance and audit readiness. |
| PCI DSS | Payment card security standards | Drives specialised PCI DSS automation solutions (e.g., Mindsec, Sprinto). |
4. Why AI and Automation Are Essential for Compliance and Security Workflows
The rise of AI-generated products and increasingly complex digital ecosystems mean manual compliance is no longer viable. Compliance automation and RegTech platforms, such as Sprinto, Vanta, and Secureframe, are essential for several reasons:
- Real-Time Monitoring: AI-powered compliance automation enables continuous, real-time monitoring, instantly flagging anomalies and enabling rapid remediation.
- Scalability: Automated platforms can handle the growing volume and complexity of regulatory frameworks, including ISO 27001, SOC 2, and PCI DSS, without proportional increases in headcount.
- Accuracy and Proactivity: AI-driven systems minimise human error, proactively detect risks, and enforce compliance before breaches occur.
- Cost Efficiency: Automation reduces the labour and time required for audits, evidence collection, and reporting, freeing up resources for innovation.
- Continuous Validation: Instead of periodic checks, AI ensures ongoing compliance validation, essential as AI-generated products proliferate and regulatory scrutiny intensifies.
With AI now building products, only AI-driven compliance automation can keep pace with the speed, scale, and complexity of modern digital businesses.
- 5. Industry and VC Momentum
- Compliance automation is evolving from a cost centre to a strategic enabler, reducing operational risk and accelerating digital transformation.
- AI and machine learning are now foundational in compliance solutions, automating evidence collection, risk assessment, and audit reporting.
- Startups like Sprinto, Vanta, and Trustero report reducing manual compliance effort by up to 90%, enabling faster and more reliable certification cycles.
- Adoption is broadening beyond technology companies into sectors such as retail, healthcare, and financial services, reflecting the universal need for scalable compliance automation and RegTech solutions.
- VC firms are prioritising startups that offer multi-framework, AI-powered platforms-especially those addressing ISO 27001, SOC 2, and PCI DSS compliance.
6. Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
- Integrating automation solutions with legacy systems and diverse regulatory environments.
- Ensuring transparency and auditability of AI-driven compliance decisions.
- Navigating overlapping and evolving regulations across jurisdictions.
- Opportunities:
- Early compliance with the EU AI Act and AMLA can be a market differentiator.
- Expansion into ESG and sustainability compliance automation as CSRD enforcement grows.
- Leveraging AI for predictive risk insights and continuous compliance monitoring.
7. Conclusion
The momentum in compliance automation and RegTech is unmistakable, with European startups and global platforms attracting record VC investment and regulatory support. As AI-driven products multiply and regulatory frameworks like ISO 27001, SOC 2, and PCI DSS become more complex, the need for automated, scalable, and proactive compliance solutions is urgent. Venture capitalists who overlook this sector risk missing out on the next wave of digital infrastructure innovation. Compliance automation is not just a regulatory necessity-it is becoming a strategic imperative for every organisation building in the digital age.
8. References & Further Reading
- Sprinto raises $20M to bring automation to security compliance management (TechCrunch)6
- Automate Your Compliance: Use Sprinto’s Cutting-Edge Solutions (Planet Compliance)8
- European Cybersecurity Investment Platform – ECSO
- VC funds investing in cybersecurity startups in Europe – Vestbee
- EU’s Cybersecurity Landscape in 2025 – Compliance Hub Wiki
- EU Releases Digital Europe Work Programmes for 2025-2027
- The Use of AI in IT Compliance Monitoring and Enforcement – Algomox
- EU Commission to Invest €1.3bn in Cybersecurity and AI
- Leveraging AI for security compliance – WeAreBrain
- Dotfile Official Website
- REMATIQ Funding Announcement
- Duna Raises €10.7M
- Vanta Funding and Product Overview
- Secureframe Series B Funding
- EU AI Act Full Text
- EU AML Package Overview
- MiCA Regulation Summary
- CSRD Directive Details
- NIS2 Directive
- PCI DSS Standards