How to select SSO Standard for your SaaS Application.
For anyone developing any application on the cloud, the major concern is always how is security implemented. Typically, you start with an authentication system viz. Usernames & Passwords. As your application grows in size of use cases and adoption, you’ll soon find a necessity to improve your security posture, these could range from MFA, Federated Identity management and finally authorisation. You now have customers who ask if you can support their AD authorisation or OneLogin or Okta etc.
This is when you’ll think about implementing a Single-Sign-On. But, the choice of how to keep data and identities secure begins much earlier for software architects and developers: selecting the standard that should be used to keep federated identities safe. This will involve two things, architecting an authorisation system – could be a separate service or bound with your application – this choice is critical to how you can grow as an organisation.
Architecture Choice:
If you choose to integrate it with your main product and 2 months later your board directs you to develop a new offering, you’ll end up doing it all over again. On the contrary, if you’re not going to pivot to any new business line, the additional time you will incur in building an external “Accounts service” will be a tax on the GTM.
Standards Choice:
IT Administrators and Security Architects must first choose the protocol or framework to use to maintain federated identity, or the mechanism of connecting a person’s electronic identity and attributes, safe while designing a plan to keep data and identities secure.
A Single Sign-On (SSO) account has the advantage of allowing employees to log in once to an application or network and not have to log in to several apps or networks during the workday. While this is beneficial to employees in terms of increasing productivity by eliminating the need to remember several passwords, it is also beneficial to IT and Security functions. The Identity and Access Management (IAM) platform responsible for maintaining employees’ credentials can assist make it more manageable by registering fewer passwords in the system.
It is, however, not an easy choice. Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML), OpenID, and open authorization are the leading candidates in the federation process (OAuth). Let’s take a closer look at these technologies and determine when SAML, OAuth, and OpenID should be used.
What is Single Sign-On (SSO)?
SSO (Single Sign-On) is an authentication method that allows apps to validate users by using other trustworthy apps. Single sign-on allows a user to use a single ID and password to log into several applications.
SSO is an important part of an Identity and Access Management (IAM) platform for managing access. User identity verification is crucial for establishing what permissions a user will have.
SSO Standards
- SAML
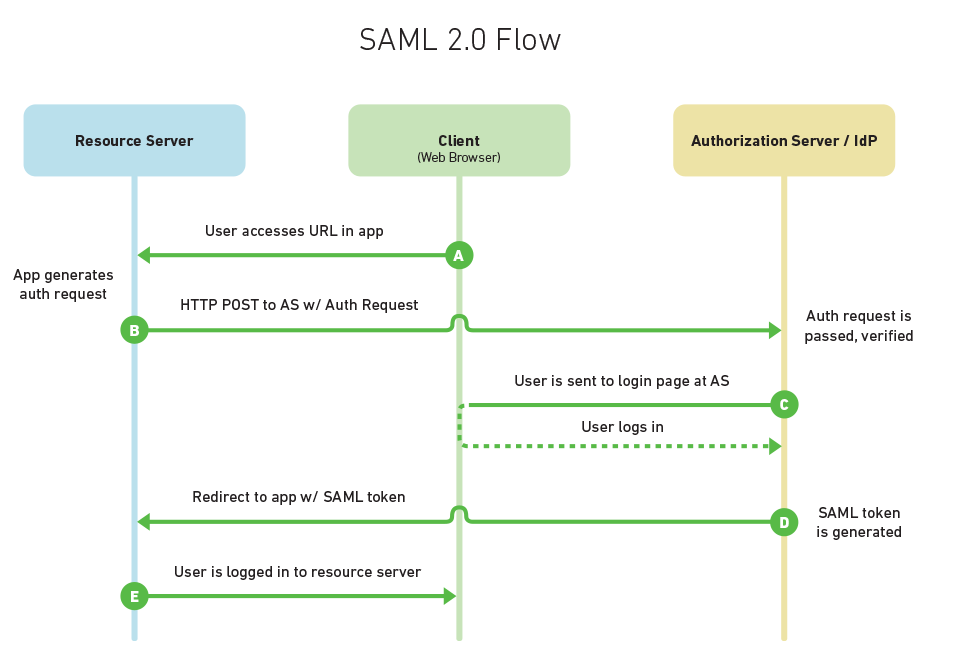
SAML is a protocol that allows an Identity Provider (IdP) to send a user’s credentials to a service provider for authentication and authorization. SAML allows for Single Sign-On (SSO) and streamlines password management. It is beneficial to businesses because employees are using an increasing number of applications to complete their tasks.
Keeping track of passwords for hundreds of programs used by hundreds, if not thousands, of employees can be difficult. SAML comes to the rescue by providing a single sign-on standard for businesses.
- OAuth
OAuth 2.0 is a secure authorization standard. It allows secure delegated access by providing third-party services with access tokens rather than exposing user credentials. It does not, however, authenticate; it just authorizes.
You’ve probably used OAuth 2.0 if you’ve ever signed up for a new app and consented to allow it automatically source fresh contacts from Facebook or your phone contacts. This standard ensures that delegated access is secure. This means that a program can operate on behalf of a user and access resources from a server without the user needing to provide their credentials. This is accomplished by allowing the Identity Provider (IdP) to issue tokens to third-party apps with the user’s permission.
- OpenID
The OpenID Connect (OIDC) standard is used for authentication. OIDC is used by identity providers (those who generate and administer identities) so that users can log in with their IdP first and then access applications without having to re-enter their credentials.
This authentication option is recognizable if you’ve used your Google account to sign in to apps like YouTube or Facebook to log into an online shopping cart. Organizations use OpenID Connect to authenticate users, and it is an open standard. This is used by IdPs so that users can sign in to the IdP and then use their sign-in information to access other websites and apps without having to log in or disclose their sign-in information.
SAML VS OAuth VS OpenID
OAuth 2.0 is a framework for regulating authorization to a protected resource, such as a program or a set of files, whereas OpenID Connect and SAML are both federated authentication industry standards. As a result, OAuth 2.0 is used in quite different situations than the other two protocols, and it can be used in conjunction with either OpenID Connect or SAML.
OpenID Connect is based on the OAuth 2.0 protocol and uses an ID token, which is a JSON Web Token (JWT) that standardizes areas where OAuth 2.0 provides for flexibility, such as scopes and endpoint discovery. It depends on user authentication and is often used to make user logins easier on consumer websites and mobile apps.
Unlike JWT, SAML does not rely on OAuth and instead relies on a message exchange to authenticate in the XML SAML format. It’s more commonly used in enterprise settings to allow users to log in to several applications with a single password.
Final Thoughts
As technology advances and systems become more interconnected, federated identification becomes increasingly useful since it is more convenient for users. It saves them time by reducing the number of accounts and passwords they have to remember, but it raises some security concerns.
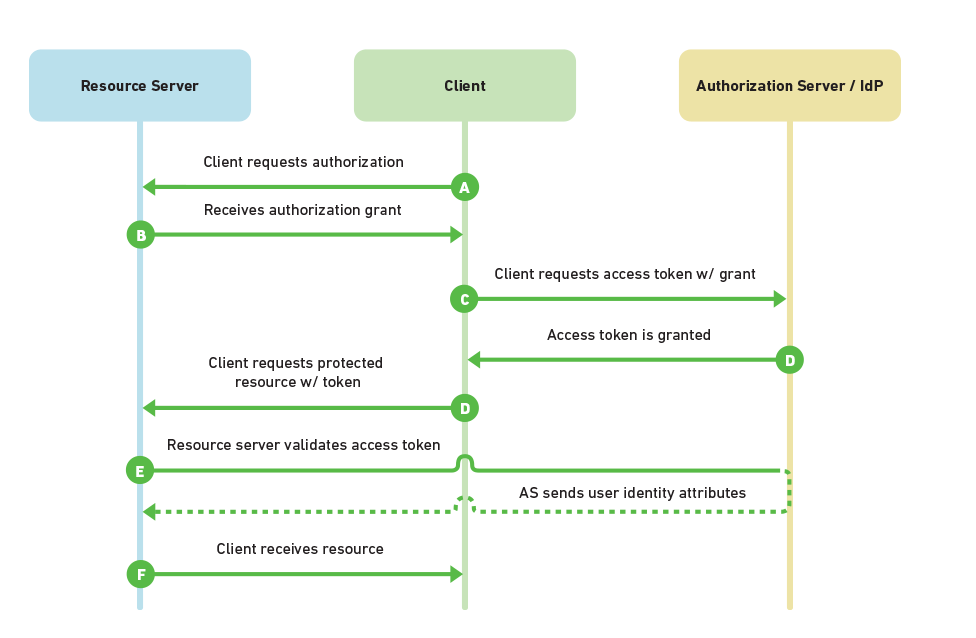
SAML has one feature that OAuth2 lacks: the SAML token contains the user identity information (because of signing). With OAuth2, you don’t get that out of the box, and instead, the Resource Server needs to make an additional round trip to validate the token with the Authorization Server.
On the other hand, with OAuth2 you can invalidate an access token on the Authorization Server, and disable it from further access to the Resource Server.
SAML provides a simpler and more standardized solution which covers all of our current and projected needs at ITILITE and avoids the use of workarounds for interoperability with native applications.